API¶
common¶
Some common framework things.
-
nmeatools.common.logged(class_)¶ Class-level decorator to insert logging.
This assures that a class has a
.logmember.@logged class Something: def __init__(self, args): self.log(f"init with {args}")
-
class
nmeatools.common.Logging(**kw)¶ Logging context manager.
with Logging(stream=sys.stderr, level=logging.INFO): do the work.
This guarantees that
logging.shutdown()is run on exit.
haversine¶
Haversine computation.
Defines a handy function for distance in Nautical Miles.
-
nmeatools.haversine.nm_haversine(lat_1, lon_1, lat_2, lon_2)¶ Computes distance in NM
Parameters: - lat_1 – Latitude of point 1
- lon_1 – Longitude of point 1
- lat_2 – Latitude of point 2
- lon_2 – Longitude of point 2
Returns: distance, NM
-
nmeatools.haversine.haversine(lat_1: float, lon_1: float, lat_2: float, lon_2: float, R: float = 3440) → float¶ Distance between points.
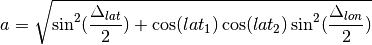
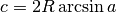
R is radius, R=MI computes in miles. Default is nautical miles.
Parameters: - lat_1 – Latitude of point 1
- lon_1 – Longitude of point 1
- lat_2 – Latitude of point 2
- lon_2 – Longitude of point 2
- R – Mean earth radius in desired units. R=NM is the default.
Returns: distance based on units of R.
>>> round(haversine(36.12, -86.67, 33.94, -118.40, R=6372.8), 5) 2887.25995
nmea_capture¶
Capture Waypoints or Routes from Chart Plotter.
usage: nmea_capture.py [-h] [--output OUTPUT] [--baud BAUD]
[--timeout TIMEOUT]
input
Options¶
-
-h,--help¶ show this help message and exit
-
--outputOUTPUT,-oOUTPUT¶ The file to write the captured NMEA data to. This will be in JSON format and can be used by waypoint_to_gpx.
-
--baudBAUD¶ BAUD setting, default is 4800
-
--timeoutTIMEOUT¶ Timeout setting, default is 2 seconds
Description¶
This an an interactive exercise between the computer capturing the data and the chartplotter producing the data.
| Chartplotter | This App |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Watch . and + to confirm receipt. |
|
-
nmeatools.nmea_capture.capture(target_file, sentence_source)¶ Write captured messages to the target file.
Parameters: - target_file – an open file to which JSON text is written.
- sentence_source – an iterable source of sentences.
-
nmeatools.nmea_capture.get_options(argv)¶ Parses command-line options.
Parameters: argv – Command-line options from sys.argv[1:].Returns: options namespace.
-
nmeatools.nmea_capture.main()¶ Main process for conversion: parse options, gather data until
^C, then writes the output file with the captured sentences.
-
nmeatools.nmea_capture.sentence_iter(options)¶ Filtered reader of sentnces. Rejects any sentences from the background list.
Currently, the reject list is:
('GPRMC', 'GPGGA', 'GPGLL', 'GPGSA', 'GPGSV', 'GPVTG', 'GPZDA', 'GPXTE')
Parameters: options – Options namespace, must have the following items. :input: the mounted device, often /dev/cu.usbserial-A6009TFG :baud: the baud rate to use, generally 4800 :timeout: the timeout, generally 2 seconds Returns: yields individual sentences that are not in a list of background messages.
nmea_data_eager¶
Define NMEA Sentences. This eagerly populates many fields from the source bytes.
Messages that are captured and (to an extent) parsed.
- $GPRMC - Recommended Minimum Specific GPS/TRANSIT Data
- $GPGGA - Global Positioning System Fix Data
- $GPGLL - Geographic position, latitude / longitude
- $GPGSA - GPS DOP and active satellites
- $GPGSV - GPS Satellites in view
- $GPVTG - Track made good and ground speed
- $GPZDA - Date & Time
- $GPXTE - Cross-track error, Measured
- $GPWPL - Waypoint (example: b‘3845.363’, b’N’, b‘07629.551’, b’W’, b’FISHTRP’)
- $GPRTE - Route
These are not (currently) interpreted.
- $GPDBT - Depth Below Transducer
- $GPDPT - Depth
- $GPMTW - Water Temperature
- $GPVHW - Water Speed and Heading
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.Decoder(*args, **kw)¶ Decode a sentence from JSON notation. This re-applies the class definition, computing and derived values from the original bytes.
Note that the JSON document doesn’t really work in bytes. We had two choices: base64 encode the original bytes, or trust that the bytes were only a subset of printable ASCII characters that overlap with UTF-8.
We chose the latter approach. The input is text, which overlaps with ASCII. We need to encode it into ASCII to recover the bytes. These are then passed to the
Sentence_Factoryto recoverSentenceinstances.>>> object = GPWPL(b'GPWPL',b'5128.62',b'N',b'00027.58',b'W',b'EGLL') >>> object GPWPL 51°28.62′N 0°27.58′W EGLL >>> text = Encoder().encode(object) >>> new_object = Decoder().decode(text) >>> new_object GPWPL 51°28.62′N 0°27.58′W EGLL
-
nmea_object_hook(as_dict)¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.Encoder(*, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, sort_keys=False, indent=None, separators=None, default=None)¶ Encode the sentence into JSON. This dumps the raw
_argsvalue, ignoring all derived values. This allows a change to the class definition; when the JSON is decoded, additional or different values will be created from the original raw data.Note that the JSON document doesn’t really work in bytes. We had two choices: base64 encode the original bytes, or trust that the bytes were only a subset of printable ASCII characters that overlap with UTF-8.
We chose the latter approach. The output is text, which overlaps with ASCII. This allows the
Sentence_Factoryand the various subclasses ofSentenceto use text internally.>>> object = GPWPL(b'GPWPL',b'5128.62',b'N',b'00027.58',b'W',b'EGLL') >>> object GPWPL 51°28.62′N 0°27.58′W EGLL >>> text = Encoder(sort_keys=True, indent=2).encode(object) >>> print(text) { "_args": [ "5128.62", "N", "00027.58", "W", "EGLL" ], "_class": "GPWPL", "_name": "GPWPL" }
-
default(obj)¶
-
log= <Logger Encoder (WARNING)>¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.Field(title, name, conversion)¶ -
conversion¶ Alias for field number 2
-
name¶ Alias for field number 1
-
title¶ Alias for field number 0
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGGA(*args)¶ Fix data
-
fields= [Field(title='UTC Time', name='time_utc', conversion=<function utc_time>), Field(title='Latitude', name='lat', conversion=<function lat>), Field(title='N/S Indicator', name='lat_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Longitude', name='lon', conversion=<function lon>), Field(title='E/W Indicator', name='lon_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Position Fix', name='fix', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Satellites Used', name='sat_used', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Horizontal dilution of precision (HDOP)', name='hdop', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Altitude in meters according to WGS-84 ellipsoid', name='alt', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Altitude Units', name='units_alt', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Geoid seperation in meters according to WGS-84 ellipsoid', name='geoid_sep', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Seperation Units', name='units_sep', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Age of DGPS data in seconds', name='age', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='DGPS Station ID', name='station', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGLL(*args)¶ Position
-
fields= [Field(title='Latitude', name='lat', conversion=<function lat>), Field(title='N/S Indicator', name='lat_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Longitude', name='lon', conversion=<function lon>), Field(title='E/W Indicator', name='lon_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='UTC Time', name='time_utc', conversion=<function utc_time>), Field(title='Status', name='status', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGSA(*args)¶ Active satellites
-
fields= [Field(title='Mode 1', name='mode1', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Mode 2', name='mode2', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Satellite used on channel PRN', name='prn_00', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN01', name='prn_01', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN02', name='prn_02', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN03', name='prn_03', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN04', name='prn_04', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN05', name='prn_05', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN06', name='prn_06', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN07', name='prn_07', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN08', name='prn_08', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN09', name='prn_09', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN10', name='prn_10', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='PRN11', name='prn_11', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Position dilution of precision (PDOP)', name='pdop', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Horizontal dilution of precision (HDOP)', name='hdop', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Vertical dilution of precision (VDOP)', name='vdop', conversion=<function nfloat>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGSV(*args)¶ Satellites in view
-
fields= [Field(title='Number of messages (1 to 9)', name='num', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Sequence number', name='seq', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Satellites in view', name='satinview', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Satellite ID 1 (1-32)', name='sat1_id', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Elevation in degrees (0-90)', name='sat1_el', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Azimuth in degrees (0-359)', name='sat1_az', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Signal to noise ration in dBHZ (0-99)', name='sat1_sn', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Satellite ID 2 (1-32)', name='sat2_id', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Elevation in degrees (0-90)', name='sat2_el', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Azimuth in degrees (0-359)', name='sat2_az', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Signal to noise ration in dBHZ (0-99)', name='sat2_sn', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Satellite ID 3 (1-32)', name='sat3_id', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Elevation in degrees (0-90)', name='sat3_el', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Azimuth in degrees (0-359)', name='sat3_az', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Signal to noise ration in dBHZ (0-99)', name='sat3_sn', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Satellite ID 4 (1-32)', name='sat4_id', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Elevation in degrees (0-90)', name='sat4_el', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Azimuth in degrees (0-359)', name='sat4_az', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Signal to noise ration in dBHZ (0-99)', name='sat4_sn', conversion=<function nint>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPRMC(*args)¶ Position and time
-
fields= [Field(title='UTC Time', name='time_utc', conversion=<function utc_time>), Field(title='Status', name='status', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Latitude', name='lat', conversion=<function lat>), Field(title='N/S Indicator', name='lat_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Longitude', name='lon', conversion=<function lon>), Field(title='E/W Indicator', name='lon_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Speed over ground', name='sog', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Course over ground', name='cog', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='UTC Date', name='date_utc', conversion=<function utc_date>), Field(title='Magnetic variation', name='mag_var', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Magnetic variation', name='mag_var_flag', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPRTE(*args)¶ GP Route
Examples:
$GPRTE,2,1,c,0,PBRCPK,PBRTO,PTELGR,PPLAND,PYAMBU,PPFAIR,PWARRN,PMORTL,PLISMR*73 $GPRTE,2,2,c,0,PCRESY,GRYRIE,GCORIO,GWERR,GWESTG,7FED*34 1 2 3 4 5 .. 1. Number of sentences in sequence 2. Sentence number 3. 'c' = Current active route, 'w' = waypoint list starts with destination waypoint 4. Name or number of the active route 5. Rest of the body is the names of waypoints in Route-
fields= [Field(title='Number of sentences in sequence', name='length', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Sentence number', name='sentence', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Current or Waypoint', name='status', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Name or Number', name='id', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPVTG(*args)¶ Course over ground
-
fields= [Field(title='Course in degrees', name='course_1', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Reference, T = True heading', name='ref_1', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Course in degrees', name='course_2', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Reference, M = Magnetic heading', name='ref_2', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Horizontal speed (SOG)', name='sog_1', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Units, N = Knots', name='units_sog_1', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Horizontal Speed (SOG)', name='sog_2', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='Units, К = Km/h', name='units_sog_2', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPWPL(*args)¶ GP Waypoint Location
Examples:
$GPWPL,4917.16,N,12310.64,W,003*65 1 2 3 1. 4917.16,N Latitude of waypoint. This is 49°16.17′N 2. 12310.64,W Longitude of waypoint. This is 123°10.64′W 3. 003 Waypoint ID $GPWPL,5128.62,N,00027.58,W,EGLL*59 1 2 3 4 5 1. 5128.62 Latitude of this waypoint 2. N North/South 3. 00027.58 Longitude of this waypoint 4. W East/West 5. EGLL Ident of this waypoint-
fields= [Field(title='Latitude', name='lat_src', conversion=<function lat>), Field(title='N/S Indicator', name='lat_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Longitude', name='lon_src', conversion=<function lon>), Field(title='E/W Indicator', name='lon_h', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Name', name='name', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPXTE(*args)¶ Cross-Track Error, Measured
-
fields= [Field(title='General warning flag', name='warning', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Not Used', name='not_used', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='cross track error distance', name='distance', conversion=<function nfloat>), Field(title='steer to correct (L/R)', name='steer', conversion=<function text>), Field(title='Units N = Nautical miles', name='units', conversion=<function text>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPZDA(*args)¶ UTC Date and Time
-
fields= [Field(title='UTC Time', name='time_utc', conversion=<function utc_time>), Field(title='Day (01 to 31)', name='day', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Month (01 to 12)', name='month', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Year', name='year', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Time zone, GMT displacement, hours (00 to ± 13)', name='tz_hr', conversion=<function nint>), Field(title='Time zone, GMT displacement, minutes', name='tz_min', conversion=<function nint>)]¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.Sentence(*args)¶ Superclass for NMEA0183 Sentences.
Each subclass provides a value for
fields. This sequence ifFieldobjects is used to convert the items in the message from bytes to useful values.There are two fields common to all sentences.
_name: The sentence type as text. The bytes are decoded from ASCII. _args: The tuple with the original argument values as Python text. These have been decoded from ASCII, which is (perhaps) not the best idea, but it makes access simple. -
fields= []¶
-
log= <Logger Sentence (WARNING)>¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.Sentence_Factory¶ Given a sequence of values, locate the class with a name that matches the sentence header and instantiate that class.
This examines all subclasses of
Sentence. The class names must match the sentence header. If there’s no match, create anUnknownSentenceinstance.Params args: The message fields. Returns: Sentenceinstance.>>> sf = Sentence_Factory() >>> fields = b'GPVTG,59.53,T,,M,0.14,N,0.3,K'.split(b',') >>> s = sf(*fields) >>> s GPVTG {'_args': ['59.53', 'T', '', 'M', '0.14', 'N', '0.3', 'K'], '_name': 'GPVTG', 'course_1': 59.53, 'course_2': None, 'ref_1': 'T', 'ref_2': 'M', 'sog_1': 0.14, 'sog_2': 0.3, 'units_sog_1': 'N', 'units_sog_2': 'K'}
-
log= <Logger Sentence_Factory (WARNING)>¶
-
sentence_class_map= {b'UnknownSentence': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.UnknownSentence'>, b'GPRMC': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPRMC'>, b'GPGGA': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGGA'>, b'GPGLL': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGLL'>, b'GPGSA': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGSA'>, b'GPGSV': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPGSV'>, b'GPVTG': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPVTG'>, b'GPZDA': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPZDA'>, b'GPXTE': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPXTE'>, b'GPWPL': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPWPL'>, b'GPRTE': <class 'nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.GPRTE'>}¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.UnknownSentence(*args)¶ Fallback for NMEA0183 Sentences that aren’t otherwise parseable.
-
log= <Logger UnknownSentence (WARNING)>¶
-
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.lat(source)¶ Convert source bytes to a latitude (deg, min) pair. Latitude: 2543.7024 = DDMM.MMMM
>>> lat(b'2543.7024') (25, 43.7024)
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.lon(source)¶ Convert source bytes to longitude (deg, mim) pair. Longitude: 08014.5267 = DDDMM.MMMM
>>> lon(b'08014.5267') (80, 14.5267)
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.nfloat(source)¶ Convert to float or None
>>> nfloat(b'') >>> nfloat(b'123.45') 123.45
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.nint(source)¶ Convert to int or None
>>> nint(b'') >>> nint(b'123') 123
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.sample_CP(listener)¶ Chart Plotter. The background message cycle is filtered out. Reads until Ctrl-C.
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.sample_GPS(listener, limit=16)¶ GPS. Displays selected messages until some limit is reached.
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.text(source)¶ Convert source bytes to text.
>>> text(b'xyz') 'xyz'
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.utc_date(source)¶ Convert source bytes to UTC date. mmddyy
>>> utc_date(b'091056') (9, 10, 56)
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_eager.utc_time(source)¶ Convert source bytes to UTC time as (H, M, S) triple HHMMSS.000
>>> utc_time(b'123456.000') (12, 34, 56.0)
nmea_data_lazy¶
Define NMEA Sentences. This lazily builds fields from the source bytes using descriptors for the individual conversions.
Messages that are captured and (to an extent) parsed.
- $GPWPL - Waypoint (example: b‘3845.363’, b’N’, b‘07629.551’, b’W’, b’FISHTRP’)
- $GPRTE - Route
These are not (currently) interpreted.
- $GPDBT - Depth Below Transducer
- $GPDPT - Depth
- $GPMTW - Water Temperature
- $GPVHW - Water Speed and Heading
- $GPRMC - Recommended Minimum Specific GPS/TRANSIT Data
- $GPGGA - Global Positioning System Fix Data
- $GPGLL - Geographic position, latitude / longitude
- $GPGSA - GPS DOP and active satellites
- $GPGSV - GPS Satellites in view
- $GPVTG - Track made good and ground speed
- $GPZDA - Date & Time
- $GPXTE - Cross-track error, Measured
Unit Tests¶
>>> class Sample(Sentence):
... f0 = Integer(1, "Item One")
... f1 = Float(2, "Item Two")
... @property
... def f2(self):
... return self.f0 + self.f1
>>> s1 = Sample(b'Sample', b'1', b'2.3')
>>> s1.f0
1
>>> s1.f1
2.3
>>> s1.f2
3.3
>>> s2 = GPWPL(b'GPWPL', b'5128.62', b'N', b'00027.58', b'W', b'EGLL')
>>> import json
>>> txt = json.dumps(s2.to_json)
>>> print(txt)
{"_class": "GPWPL", "_args": ["GPWPL", "5128.62", "N", "00027.58", "W", "EGLL"]}
>>> obj = json.loads(txt, object_hook=decode)
>>> print(obj)
GPWPL 51°28.62′N 0°27.58′W EGLL
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Field(position, title, name=None, conversion=<function Field.<lambda>>)¶ Define a field. Provide the position, a description, and a conversion rule.
The name is there to parallel the
nmea_dataNamedtuple implementation.Subclasses should include conversions directly. This can be used with conversion plug-in functions.
f = Text(1, "Description")is better thanf = Field(1, "Description", "f", text)which is better thanf = Field(1, "Description", "f", lambda b: b.decode('ascii'))>>> class Sample(Sentence): ... f = Field(1, "title", "f", lambda b: b.decode('ascii')) >>> s = Sample(b'Sample', b'text') >>> s.f 'text'
-
static
transform(func, value)¶
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Float(position, title)¶ -
static
nfloat(value)¶ Convert to float or None
>>> Float.nfloat(b'') >>> Float.nfloat(b'123.45') 123.45
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.GPRTE(*args)¶ GP Route
Examples:
$GPRTE,2,1,c,0,PBRCPK,PBRTO,PTELGR,PPLAND,PYAMBU,PPFAIR,PWARRN,PMORTL,PLISMR*73 $GPRTE,2,2,c,0,PCRESY,GRYRIE,GCORIO,GWERR,GWESTG,7FED*34 1 2 3 4 5 .. 1. Number of sentences in sequence 2. Sentence number 3. 'c' = Current active route, 'w' = waypoint list starts with destination waypoint 4. Name or number of the active route 5. Rest of the body is the names of waypoints in Route-
id= None¶
-
length= None¶
-
sentence= None¶
-
status= None¶
-
waypoints¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.GPWPL(*args)¶ GP Waypoint Location
Examples:
$GPWPL,4917.16,N,12310.64,W,003*65 1 2 3 1. 4917.16,N Latitude of waypoint. This is 49°16.17′N 2. 12310.64,W Longitude of waypoint. This is 123°10.64′W 3. 003 Waypoint ID $GPWPL,5128.62,N,00027.58,W,EGLL*59 1 2 3 4 5 1. 5128.62 Latitude of this waypoint 2. N North/South 3. 00027.58 Longitude of this waypoint 4. W East/West 5. EGLL Ident of this waypoint-
lat_angle= None¶
-
lat_h= None¶
-
latitude¶ Two source fields are combined: the angle and the hemisphere (N/S).
-
lon_angle= None¶
-
lon_h= None¶
-
longitude¶ Two source fields are combined: the angle and the hemisphere (E/W).
-
name= None¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Integer(position, title)¶ -
static
nint(value)¶ Convert to int or None
>>> Integer.nint(b'') >>> Integer.nint(b'123') 123
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.LatAngle(position, title)¶ Note that the hemisphere information (N/S) isn’t present.
-
static
lat(source)¶ Convert source bytes to latitude (deg, min) pair. Latitude: 2543.7024 = DDMM.MMMM
>>> LatAngle.lat(b'2543.7024') (25, 43.7024)
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Latitude(pos_angle, pos_h, title)¶ Two source fields are combined: the angle and the hemisphere (N/S).
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.LonAngle(position, title)¶ Note that the hemisphere information (E/W) isn’t present.
-
static
lon(source)¶ Convert source bytes to longitude (deg, min) pair. Longitude: 08014.5267 = DDDMM.MMMM
>>> LonAngle.lon(b'08014.5267') (80, 14.5267)
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Longitude(pos_angle, pos_h, title)¶ Two source fields are combined: the angle and the hemisphere (E/W).
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Sentence(*args)¶ >>> class Sample(Sentence): ... f0 = Integer(1, "Item One") ... f1 = Float(2, "Item Two") ... @property ... def f2(self): ... return self.f0 + self.f1 >>> s = Sample(b'Sample', b'1', b'2.3') >>> s.f0 1 >>> s.f1 2.3 >>> s.f2 3.3
Can be converted from original fields = [...] lists.
>>> class Sample2(Sentence): ... f0 = Field(1, "Item One", "f0", int) ... f1 = Field(2, "Item Two", "f1", float) ... @property ... def f2(self): ... return self.f0 + self.f1 >>> s = Sample2(b'Sample', b'1', b'2.3') >>> s.f0 1 >>> s.f1 2.3 >>> s.f2 3.3
-
log= <Logger Sentence (WARNING)>¶
-
to_json¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Sentence_Factory¶ Given a sequence of values, locate the class with a name that matches the sentence header and instantiate that class.
This examines all subclasses of
Sentence. The class names must match the sentence header. If there’s no match, create anUnknownSentenceinstance.Params args: The message fields. Returns: Sentenceinstance.>>> sf = Sentence_Factory() >>> fields1 = b'GPVTG,59.53,T,,M,0.14,N,0.3,K'.split(b',') >>> s1 = sf(*fields1) >>> s1 UnknownSentence(*(b'GPVTG', b'59.53', b'T', b'', b'M', b'0.14', b'N', b'0.3', b'K'))
>>> fields2 = b'GPWPL', b'5128.62', b'N', b'00027.58', b'W', b'EGLL' >>> s2 = sf(*fields2) >>> s2 GPWPL 51°28.62′N 0°27.58′W EGLL
-
log= <Logger Sentence_Factory (WARNING)>¶
-
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.Text(position, title)¶ -
static
text(value)¶ >>> Text.text(b'xyz') 'xyz'
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.UTC_Date(position, title)¶ -
static
utc_date(source)¶ Convert source bytes to UTC date. mmddyy
>>> UTC_Date.utc_date(b'091056') (9, 10, 56)
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.UTC_Time(position, title)¶ -
static
utc_time(source)¶ Convert source bytes to UTC time as (H, M, S) triple HHMMSS.000
>>> UTC_Time.utc_time(b'123456.000') (12, 34, 56.0)
-
static
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.UnknownSentence(*args)¶ Fallback for NMEA0183 Sentences that aren’t otherwise parseable.
-
log= <Logger UnknownSentence (WARNING)>¶
-
-
nmeatools.nmea_data_lazy.decode(object)¶
nmea_device¶
Listener to NMEA interface.
Here’s an example of NMEA 0183 to USB hardware.
PySerial is required. Using PySerial 3.3. https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pyserial
Typical interface to NMEA 0183 requires this kind of serial interface:
- Typical Baud rate 4800
- Data bits 8
- Parity None
- Stop bits 1
- Handshake None
We’ll decode NMEA 0183 Sentences. See http://www.robosoft.info/en/technologies/knowledgebase/nmea0183
The checksum is the bitwise exclusive OR of ASCII codes of all characters between the $ and *.
This is done with reduce(operator.xor, bytes)
The listener is an Interator as well as a Context Manager.
Also – since messages are ”,”-separated, it handles the split operation.
Reference¶
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NMEA_0183
See http://www.gpsinformation.org/dale/nmea.htm#nmea
See http://www.catb.org/gpsd/NMEA.html
See https://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/GPS/NMEA%20Reference%20Manual1.pdf
Unit Test¶
Note the subtle complexity of passing end-of-line in a string to doctest. We can’t simply use `` `` in a sample input string, or the compiler being used by doctest gets confused.
Good Messages:
>>> m0= b'''$GPRMC,162823.000,A,2542.9243,N,08013.6310,W,0.14,59.53,180214,,*2F
... '''
>>> m1= b'''$GPVTG,59.53,T,,M,0.14,N,0.3,K*5C
... '''
>>> m2= b'''$GPGGA,162824.000,2542.9243,N,08013.6311,W,1,06,1.5,3.3,M,-27.3,M,,0000*6E
... '''
>>> m3= b'''$GPGLL,2542.9243,N,08013.6310,W,162823.000,A*29
... '''
>>> m4= b'''$GPGSA,A,3,29,24,18,14,22,27,,,,,,,2.9,1.5,2.5*3E
... '''
>>> m5= b'''$GPGSV,3,1,10,21,82,249,18,24,54,090,37,18,52,343,33,15,32,039,34*7D
... '''
>>> m6= b'''$GPGSV,3,2,10,14,28,244,36,22,27,307,33,29,12,190,32,06,10,293,28*74
... '''
>>> m7= b'''$GPGSV,3,3,10,27,08,303,27,12,00,139,25*7F
... '''
>>> Listener.validate(m0)
(b'GPRMC', b'162823.000', b'A', b'2542.9243', b'N', b'08013.6310', b'W', b'0.14', b'59.53', b'180214', b'', b'')
>>> Listener.validate(m1)
(b'GPVTG', b'59.53', b'T', b'', b'M', b'0.14', b'N', b'0.3', b'K')
>>> Listener.validate(m2)
(b'GPGGA', b'162824.000', b'2542.9243', b'N', b'08013.6311', b'W', b'1', b'06', b'1.5', b'3.3', b'M', b'-27.3', b'M', b'', b'0000')
>>> Listener.validate(m4)
(b'GPGSA', b'A', b'3', b'29', b'24', b'18', b'14', b'22', b'27', b'', b'', b'', b'', b'', b'', b'2.9', b'1.5', b'2.5')
>>> Listener.validate(m5)
(b'GPGSV', b'3', b'1', b'10', b'21', b'82', b'249', b'18', b'24', b'54', b'090', b'37', b'18', b'52', b'343', b'33', b'15', b'32', b'039', b'34')
>>> Listener.validate(m6)
(b'GPGSV', b'3', b'2', b'10', b'14', b'28', b'244', b'36', b'22', b'27', b'307', b'33', b'29', b'12', b'190', b'32', b'06', b'10', b'293', b'28')
>>> Listener.validate(m7)
(b'GPGSV', b'3', b'3', b'10', b'27', b'08', b'303', b'27', b'12', b'00', b'139', b'25')
Broken Message, typical case:
>>> b0= b'''42.9243,N,08013.6310,W,0.14,59.53,180214,,*2F
... '''
>>> x= Listener.validate(b0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6/doctest.py", line 1330, in __run
compileflags, 1), test.globs)
File "<doctest __main__[16]>", line 1, in <module>
x= Scanner.validate(b0)
File "gps_spike.py", line 143, in validate
assert sentence_bytes.startswith(b'$'), "Sentence Fragment"
AssertionError: Sentence Fragment
-
class
nmeatools.nmea_device.Listener(options)¶ Listen to the device, yielding a sequence of sentences.
This is an Interable and a Context Manager for listening to an NMEA-0183 device.
The typical use case is this
with Listener(options) as GPS: for sentnce in GPS: print(sentence)
-
log= <Logger Listener (WARNING)>¶
-
static
validate(sentence_bytes)¶ Validate an NMEA sentence, returning either a tuple of substrings or an
AssertionError.Parameters: sentence_bytes – A bytes object with the raw sentence. Returns: tuple with individual fields, suitable for use with a Sentence_Factoryisntance.Raises: AssertionError – If the sentence is incomplete in some way.
-
waypoint_merge¶
Merge waypoints from two sources:
- The master GPX file. These have precedence. Any duplicates here create warnings.
- A new GPX file. Duplicates from here are dropped.
The output is a combined list with duplicated locations removed. This becomes the new master.
-
class
nmeatools.waypoint_merge.Waypoint(lat, lon, name, time, sym)¶ Behaves a little bit like an NMEA GPWPL sentence.
-
args¶
-
distance(other)¶ Distance in NM.
-
log= <Logger Waypoint (WARNING)>¶
-
-
nmeatools.waypoint_merge.merge(master_path=PosixPath('/Volumes/NO NAME/WaypointsRoutesTracks.gpx'), update_path=PosixPath('/Users/slott/Documents/Sailing/Cruise History/routes/waypoints.gpx'))¶
-
nmeatools.waypoint_merge.waypoint_iter(root, namespace)¶
waypoint_to_gpx¶
Convert waypoints or routes to GPX format for iNavX/GPSNavX
Synopsis¶
usage: waypoint_to_gpx.py [-h] --desc DESC [--force]
[--format {.gpx,.csv,.kml}]
[input [input ...]]
Arguments¶
-
input¶ One or more files to convert. These must be JSON-format files created by the nmea_capture program.
Options¶
optional arguments:
-
-h,--help¶ show this help message and exit
-
--descDESC,-dDESC¶ Description
-
--force¶ Force overwrite of the .gpx output file.
-
--format{.gpx,.csv,.kml},-f{.gpx,.csv,.kml}¶ The output formaat. Currently, only .gpx is supported and it’s the default.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.build_gpx(document, name, description)¶ Create the
<gpx>Element, inserting metadata.Parameters: - document – The root document
- name – The string name to put in the metadata
- description – the string description to put in the metadata
Returns: the
<gpx>element
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.build_routepoint(document, s, sym=None)¶ Create a
<rtept>element, inserting a<name>element (optionally a<sym>).Parameters: - document – The root document
- s – An
nmeatools.nmea_data.GPWPLinstance. - sym – An optional string with a symbol name to include.
Returns: the
<rtept>e,ement
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.build_waypoint_location(document, s)¶ Create a
<wpt>element, inserting a<name>element.Parameters: - document – The root document
- s – An
nmeatools.nmea_data.GPWPLinstance.
Returns: the
<wpt>e,ement
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.convert_route(route_path, description='2017 Waypoints from Red Ranger chartplotter.')¶ Load JSON document with GPWPL and GPRTE sentences; return GPX representation.
Parameters: - route_path – Path with location of routes in JSON notation.
- description – Description to insert into the metadata.
Returns: root document with
<gpx>and<rte>and<rtept>tags.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.convert_waypoints(waypoints_path, description='2017 Waypoints from Red Ranger chartplotter.')¶ Load JSON document with GPWPL sentences; return GPX representation.
Parameters: - waypoints_path – Path with location of waypoints in JSON notation.
- description – Description to insert into the metadata.
Returns: root document with
<gpx>and<wpt>tags.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.get_options(argv)¶ Parses command-line options.
Parameters: argv – Command-line options from sys.argv[1:].Returns: options namespace.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.main()¶ Main process for conversion: parse options, process files. Only the GPX output is supported currently.
Each file is scanned to see what it contains.
- ‘GPRTE’, ‘GPWPL’ – a route
- ‘GPWPL’ – only waypoints
The output path matches the input path with a suffix changed to
.gpx.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.route_to_gpx(sentences, name, description)¶ Create GPX doc with a route that contains waypoints.
- Save waypoint as {name : sentence} map.
- Flatten route sentences into a single list of waypoints.
This presumes the
nmeatools.nmea_data.GPRTEsentences are already in their proper order.
Parameters: - sentences – iterable sequence of
nmeatools.nmea_data.GPWPLandnmeatools.nmea_data.GPRTEinstances - name – The string name to put in the metadata
- description – the string description to put in the metadata
Returns: <gpx>element containing the<rte>and<rtpte>waypoints.
-
nmeatools.waypoint_to_gpx.waypoints_to_gpx(sentences, name, description)¶ Create GPX doc with waypoints.
Parameters: - sentences – iterable sequence of
nmeatools.nmea_data.GPWPLinstances - name – The string name to put in the metadata
- description – the string description to put in the metadata
Returns: <gpx>element containing the<wpt>waypoints.- sentences – iterable sequence of